The 3B Scientific W DNARNA stationary model includes interlocking parts and a wooden stand This model demonstrates the structure of DNA and RNA molecules Interlocking pieces connect to form the double helix shape and show how molecules split atDNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides, each of which is usually symbolized by a single letter either A, T, C, or G Chargaff's rules state that DNA from any species of any organism should have a 11 protein stoichiometry ratio (base pair rule) of purine and pyrimidine bases (ie, AT=GC) and, more specifically, that the amount of guanine should beSep 18, 08 · 111 DNA and RNA Structure and Function Your DNA contains the recipes for the proteins that your cells make A segment of DNA that contains the recipe for building one protein is called a gene Genes occur on chromosomes Mutations in genes can cause metabolic errors and genetic diseases

Dna Vs Rna Biology Dictionary
Study of models on dna and rna structure
Study of models on dna and rna structure-Feb 09, 14 · Structure of Doublehelix Three major forms BDNA ADNA ZDNA BDNA is biologically THE MOST COMMON It is a helix meaning that it has a Right handed, or clockwise, spiral Complementary base pairing • AT • GC Ideal BDNA has 10 base pair per turn(360o rotation of helix) So each base is twisted 36o relative to adjacent bases Base pair are 034 nmThe two main types of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA Both DNA and RNA are made from nucleotides, each containing a fivecarbon sugar backbone, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base DNA provides the code for the cell's activities, while RNA converts that code into proteins to carry out cellular functions The sequence of nitrogen bases (A, T, C, G) in DNA is what forms an



3
May 14, 15 · The Structure of RNA There is a second nucleic acid in all cells called ribonucleic acid, or RNA Like DNA, RNA is a polymer of nucleotides Each of the nucleotides in RNA is made up of a nitrogenous base, a fivecarbon sugar, and a phosphate group In the case of RNA, the fivecarbon sugar is ribose, not deoxyriboseMar 11, 18 · Mar 11, 18 · Modeling DNA and RNA Structure with Gummy Bears This activity uses candy to allow students to assemble and then compare and contrast the DNA and RNA Structure Students often find the structure of these tiny molecules hard to visualize, let alone remembering what constitutes an individual nucleotide!Watson and Crick (1953) have proposed a model for the structure of DNA molecule which is now usually accepted by all According to this model called as Watson Crick Model, the DNA molecule is a double helix structure consisting of two long polynucleotide chains coiled round each other around an imaginary axis and running opposite to each other
Jun 03, 21 · Predominant Structure The DNA is a doublestranded molecule that has a long chain of nucleotides The RNA is a singlestranded molecule which has a shorter chain of nucleotides Propagation DNA replicates on its own, it is selfreplicating RNA does not replicate on its own It is synthesized from DNA when required Nitrogenous Bases and PairingStart studying DNA and RNA Structure Quiz Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsMar 02, 13 · Structural Characteristics ofmRNA(Contd) The m RNA molecules are formed with the help ofDNA template during the process of transcription The sequence of nucleotides in m RNA iscomplementary to the sequence of nucleotides ontemplate DNA The sequence carried on m RNA is read in the formof codons A codon is made up of 3 nucleotides The mRNA is formed after processing ofheterogeneous nuclear RNA
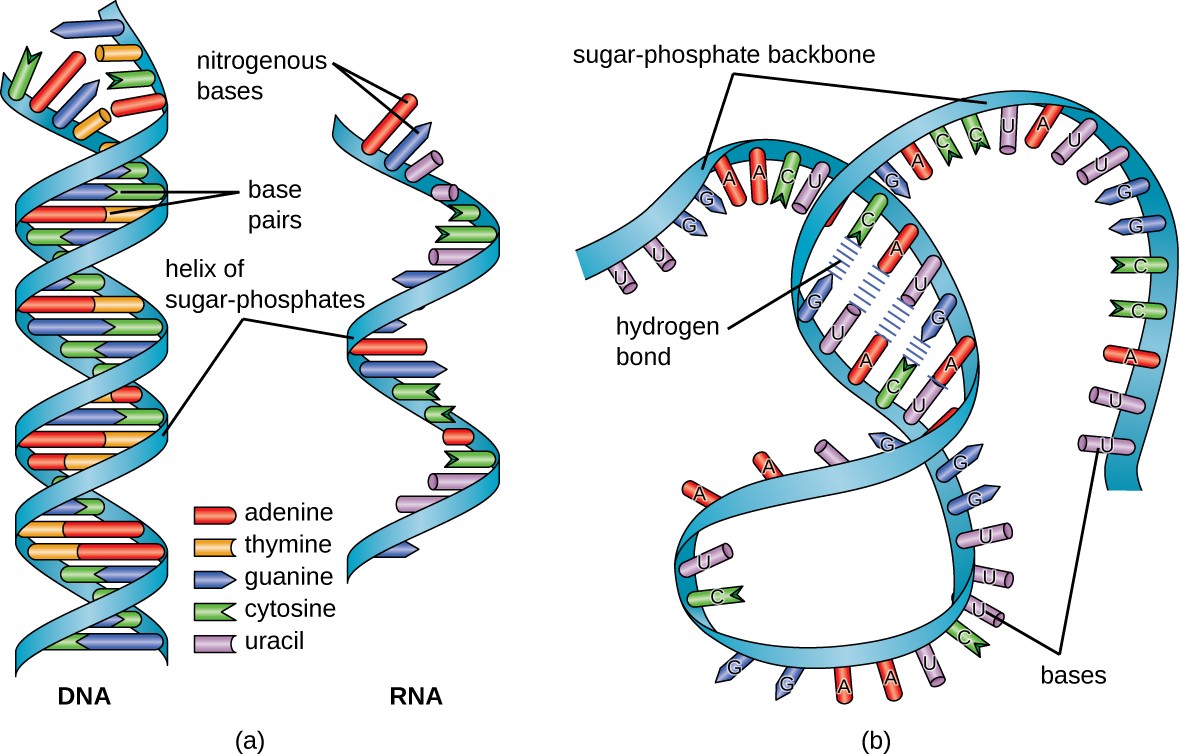
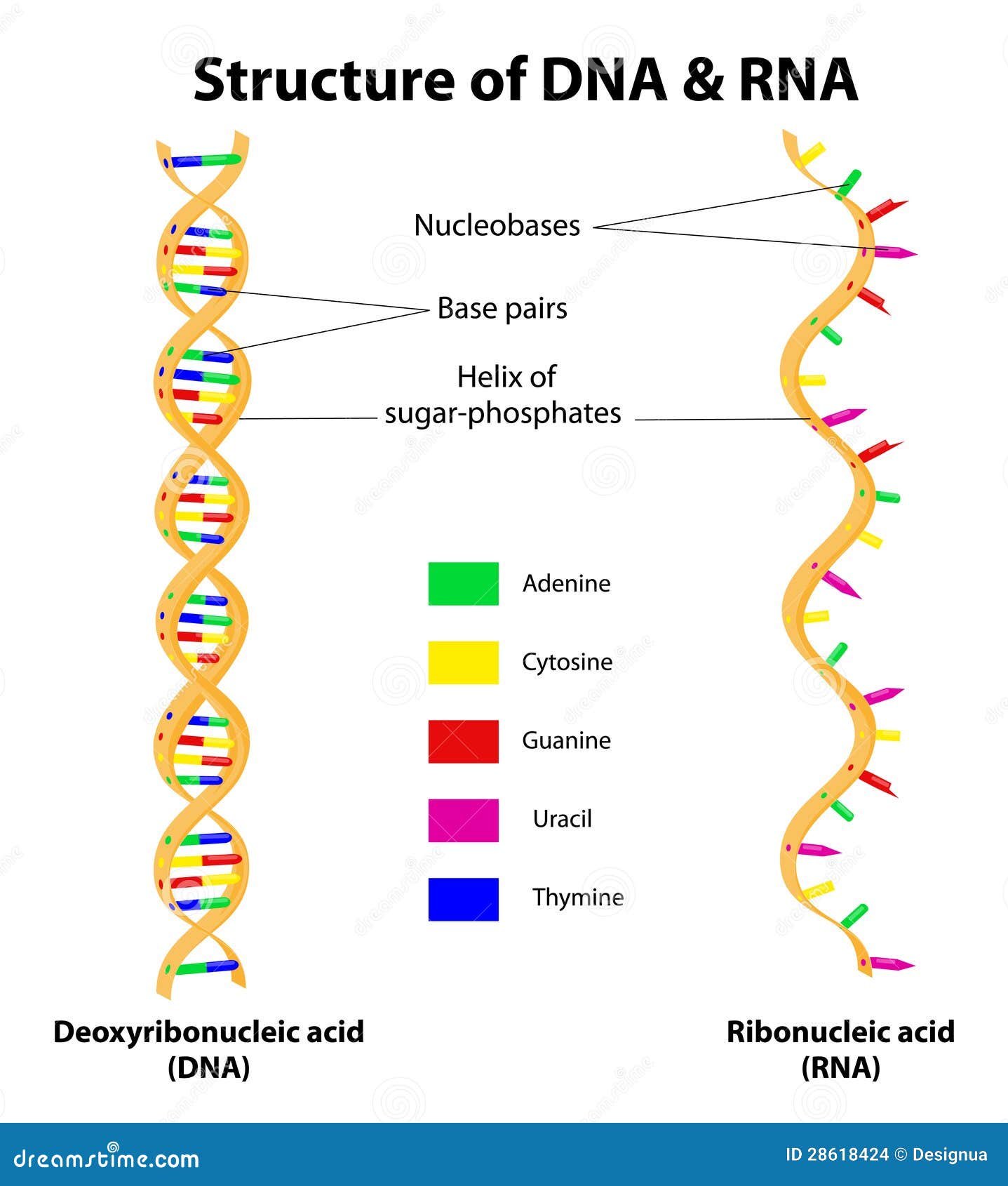
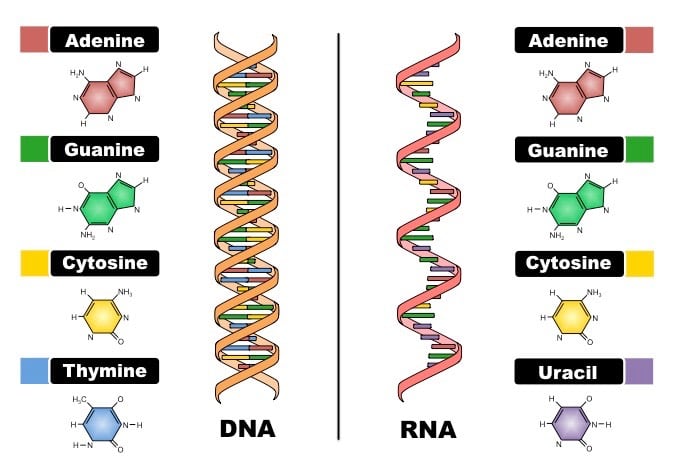
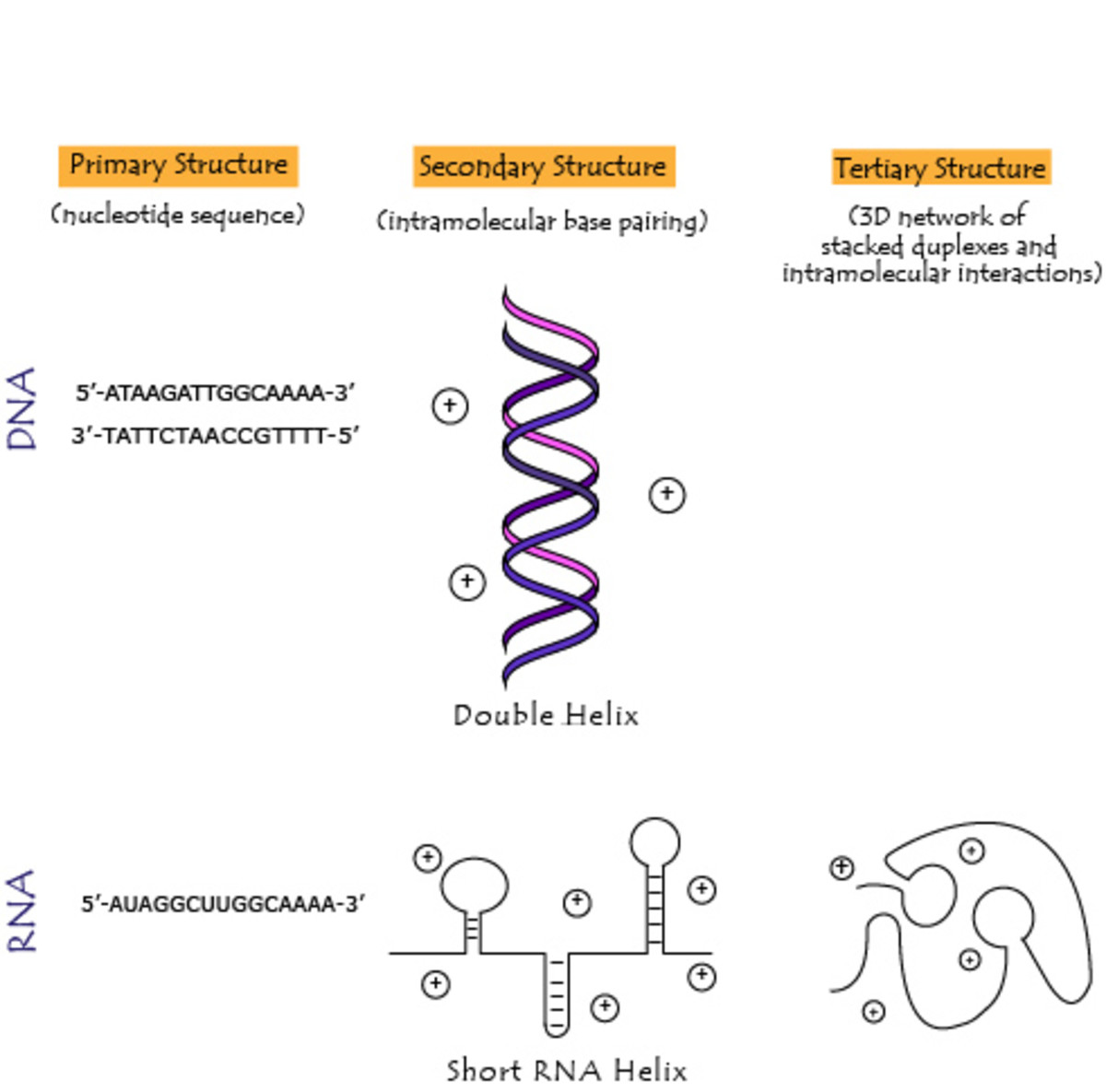
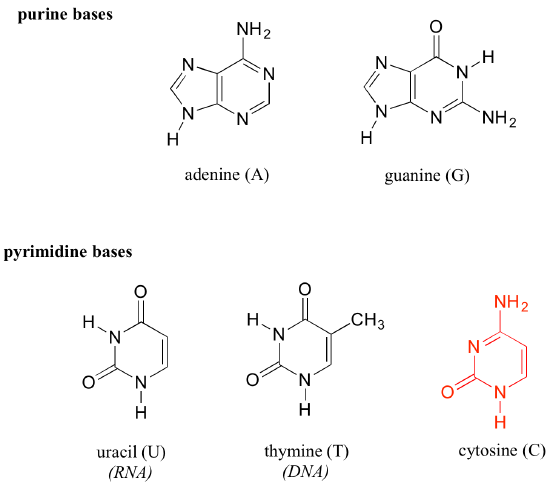
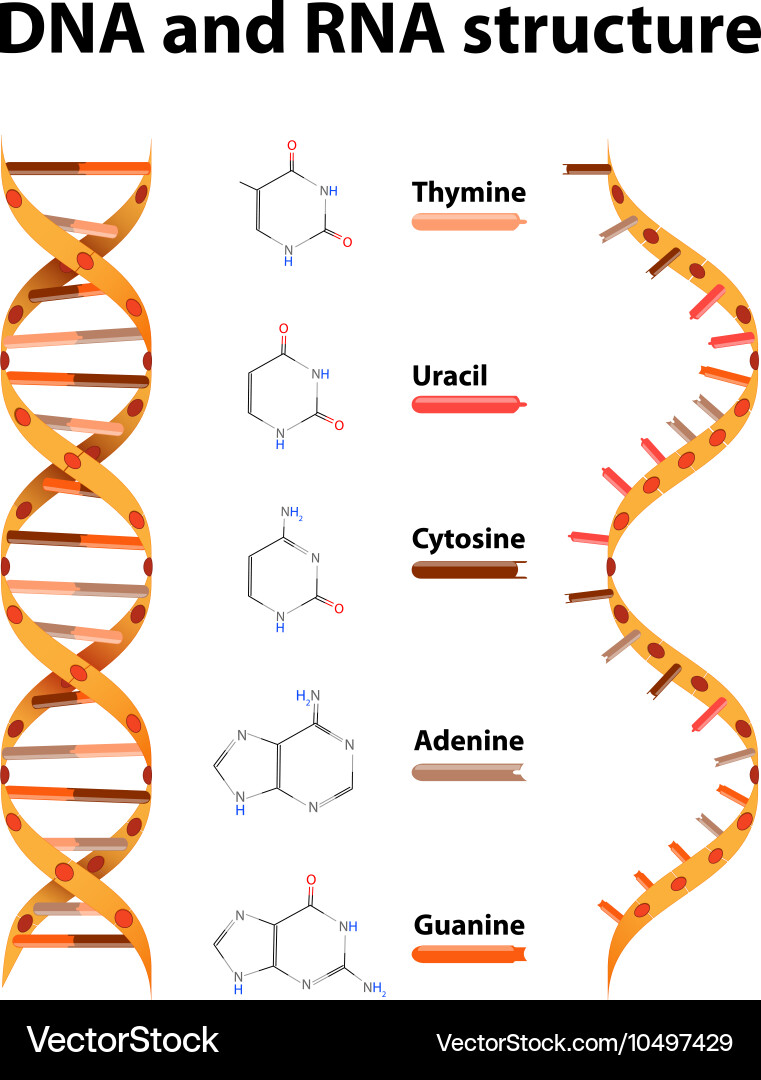
Apr 16, 11 · DNA and RNA are two types of nucleic acids present in living organisms DNA is present in the nucleus of eukaryotes while RNA is present in the cytoplasm A major difference between DNA and RNA structure is in their monomers Deoxyribonucleotide is the basic unit of DNA while ribonucleotide is the basic unit of RNANucleic acids have a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure analogous to the classification of protein structure The sequence of bases in the nucleic acid chain gives the primary structure of DNA or RNA The sequence of bases is read in a 5′ → 3′ direction, so that you would read the structure in the next figure as ACGT See Figure 1RNA molecules are relatively short in length compared with DNA RNAs tend to form a hundred to thousands of nucleotides long, depending on their partucular role RNA is a single strand polynucleotide in which the sugar is ribose The bases found in RNA are cytosine, adenine, guanine and uracil (uracil replaces thymine in the cell)



Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology




Dna Vs Rna Differences Similarities Expii
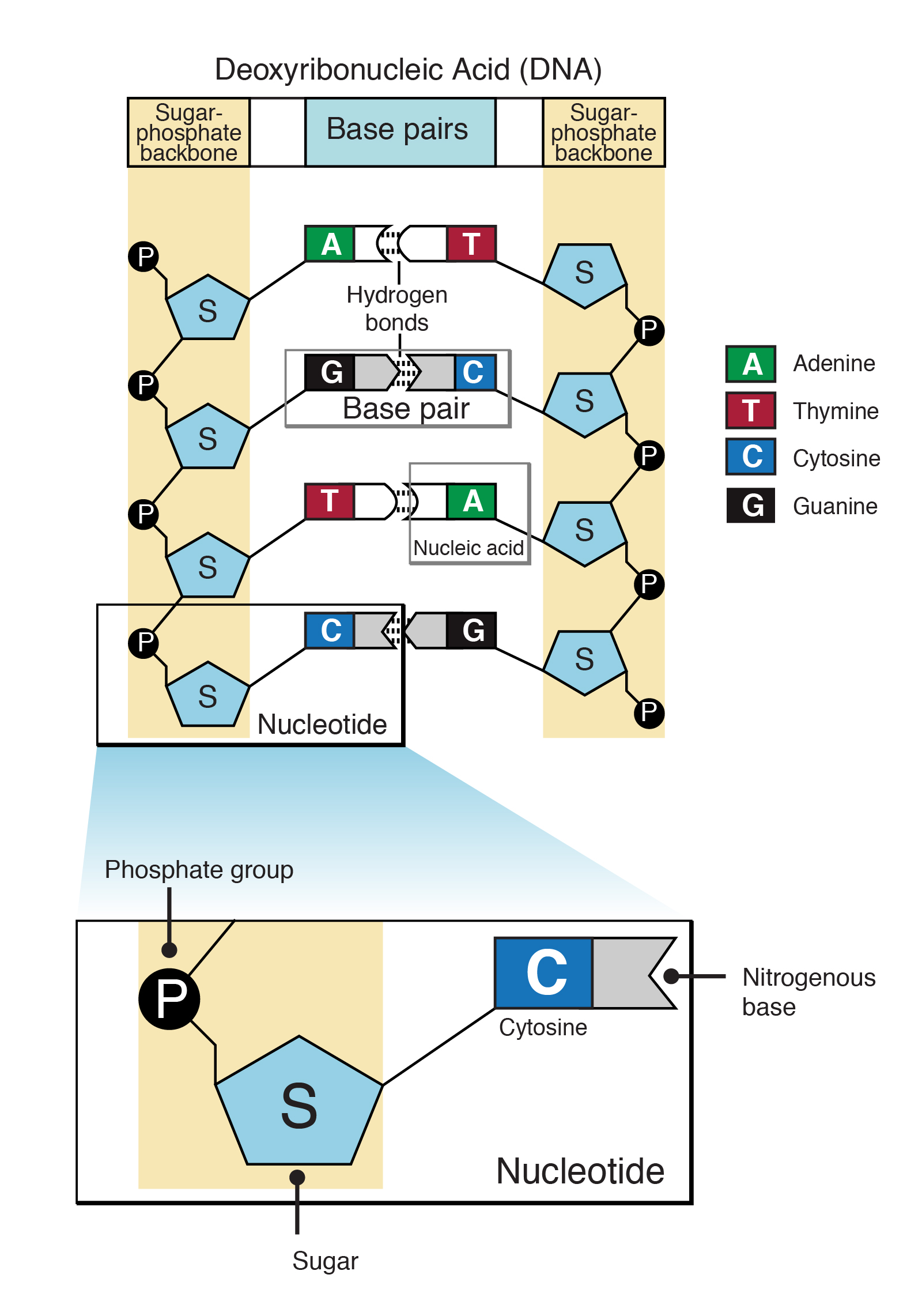
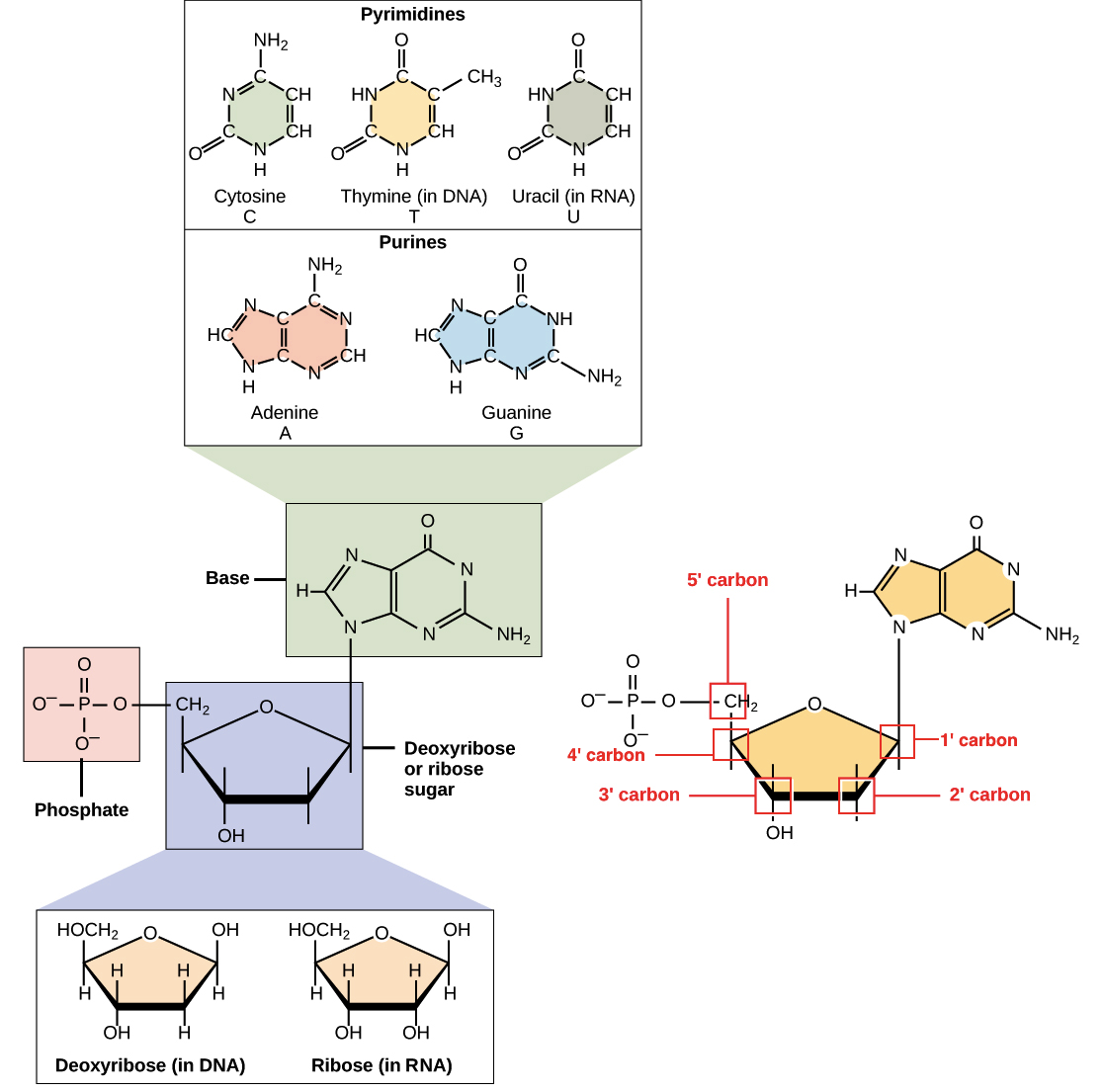
Feb 24, 06 · The tRNA PHE structure is notable in the field of nucleic acid structure in general, as it represented the first solution of a longchain nucleic acid structure of any kind RNA or DNA preceding Richard E Dickerson's solution of a Bform dodecamer by nearly a decadeDNA Structure DNA has three main components 1 Deoxyribose (a pentose sugar) 2 Base (there are four different ones) 3 Phosphate DNA structure is often divided into four different levels primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternaryMay 28, 21 · May 28, 21 · 11 The Structure of DNA Identify the sugar, phosphate, nitrogenous base, 5' and 3' carbons in a nucleotide and the key difference between DNA and RNA Explain the structure of the double helix, including the role of hydrogen bonds and covalent (phosphodiester) bonds Explain why the abundance of A is roughly equal to T and G is roughly



Types Of Rna Mrna Rrna And Trna



1
Jun 19, 18 · Watson and Crick model of DNA In April 1953, Watson and Crick published a paper on the threedimensional structure of DNA which was the first report explained the molecular structure of DNA DNA is a helical structure in which two helices twisted around one another on the same axis in a righthanded mannerApr 01, 19 · The diversity of DNA and RNA sequences dictates their structures, which in turn control their binding specificity to proteins The structure of protein–DNA complexes may vary and sometimes even small nuances in the geometrical parameters of the major or minor grooves are fundamental to achieving specificity 1,2 andIn this video we cover the structure of nucleic acids, DNA and RNA We discuss the components of each, and the differences between the twoTranscript with n



Structure Dna And Rna Molecule Vector Stock Vector Illustration Of Human Education



Dna Vs Rna Differences Similarities Expii
RNA pairs with DNA, G and C always pair together, T in DNA always pairs with A in RNA, but A in DNA pairs with U in RNA When RNA pairs with RNA, then G pairs with C and A pairs with U Third, RNAissinglestranded(usually)whileDNAisdoublestranded That is, RNA does not have the ladderlike structure of the DNA in Figure 31 Instead, RNA would look like Figure 41 after the ladderWe already have an overview video of DNA and I encourage you to watch that first but what I want to do in this video is dig a little bit deeper actually get into the molecular structure of DNA and just as a starting point let's just remind ourselves what DNA stands for all right the different parts of the word in different colors so it stands for deoxy deoxyribonucleic ribonucleic ribonucleicChromosomal DNA consists of two DNA polymers that make up a 3dimensional (3D) structure called a double helix In a double helix structure, the strands of DNA run antiparallel, meaning the 5' end of one DNA strand is parallel with the 3' end of the other DNA strand



Rna Structure And Function




Dna Vs Rna Biology Dictionary
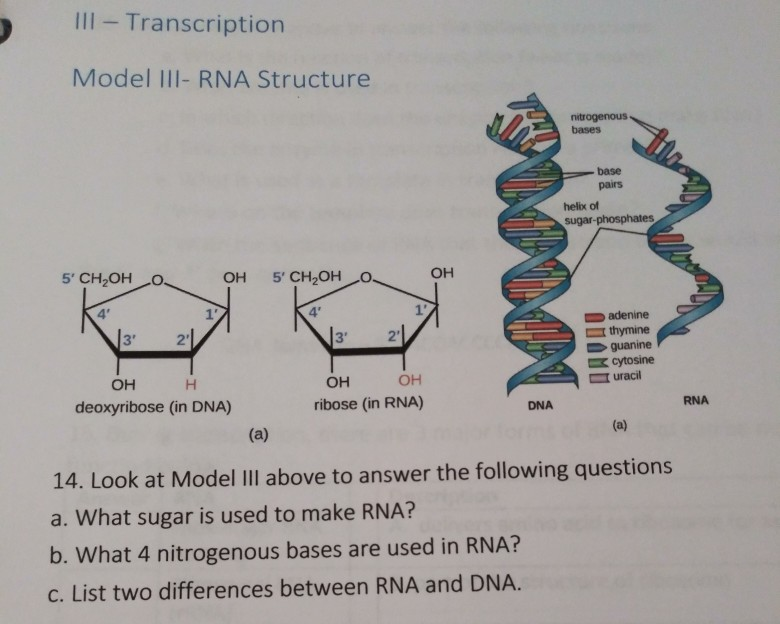
Summary DNA is the most important nucleic acid present in living organisms The structure of DNA was best explained by Watson and Crick model According to this model, DNA is made up of two polynucleotide chains that are wound around each other in an antiparallel fashion to form aDNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs 26A1 Crick and Watson's elucidation of the structure of DNA using model making 26S1 Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to26A1 Crick and Watson's elucidation of the structure of DNA using model making 26S1 Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to represent phosphates, and pentoses and bases
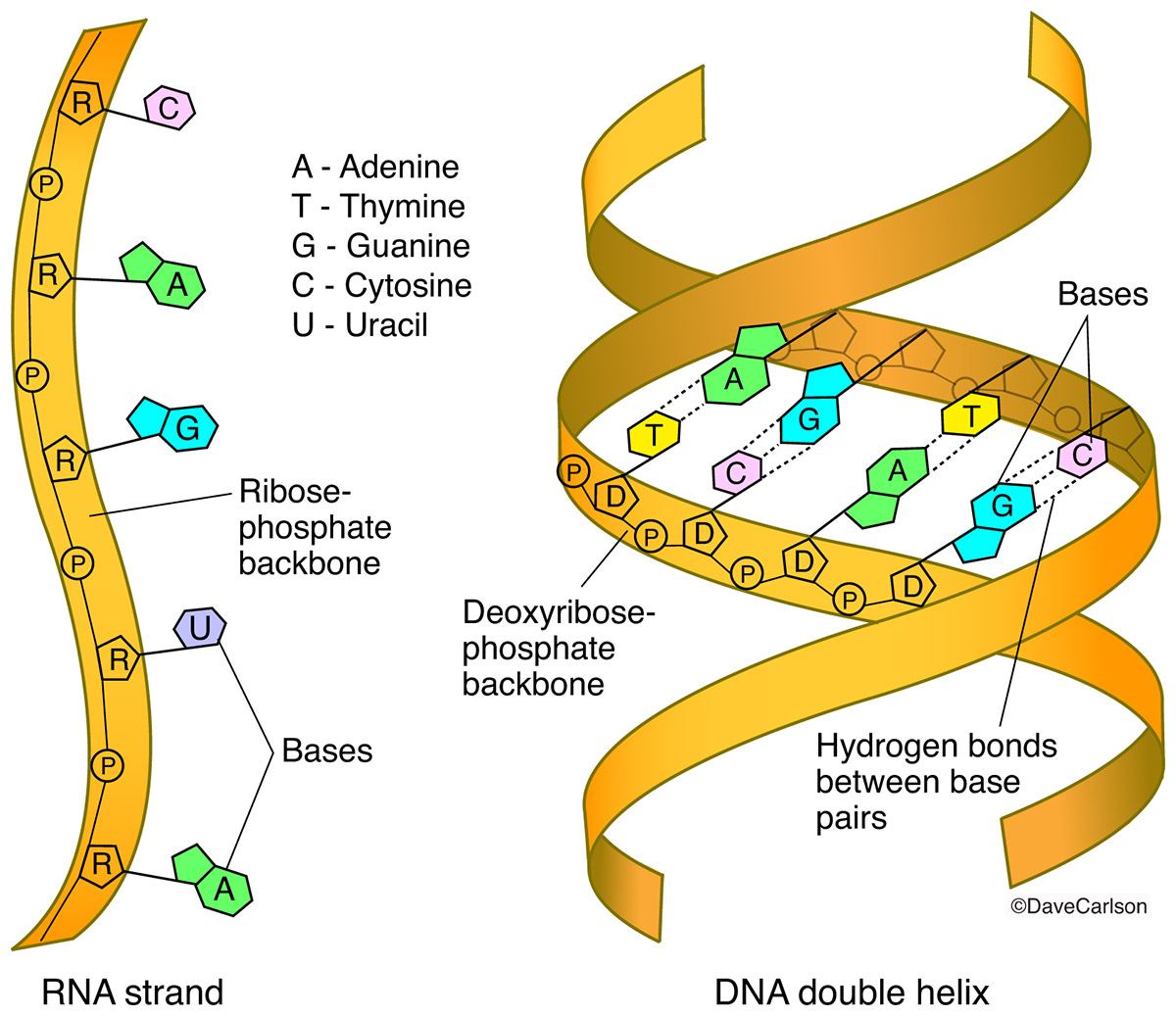



Dna Rna Structure Carlson Stock Art




Structure Of Dna Rna And Arabinonucleic Acids Ana Download Scientific Diagram
Allowing them to construct a physical modelInstead they are replaced by uracil 3) the DNA molecule normally appears as a double strand, whileThe structure of DNA was determined by American geneticist James Watson and British biophysicist Francis Crick in 1953 Watson and Crick based their model largely on the research of British physicists Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins, who analyzed Xray diffraction patterns to show that DNA is a double helix The findings of Chargaff
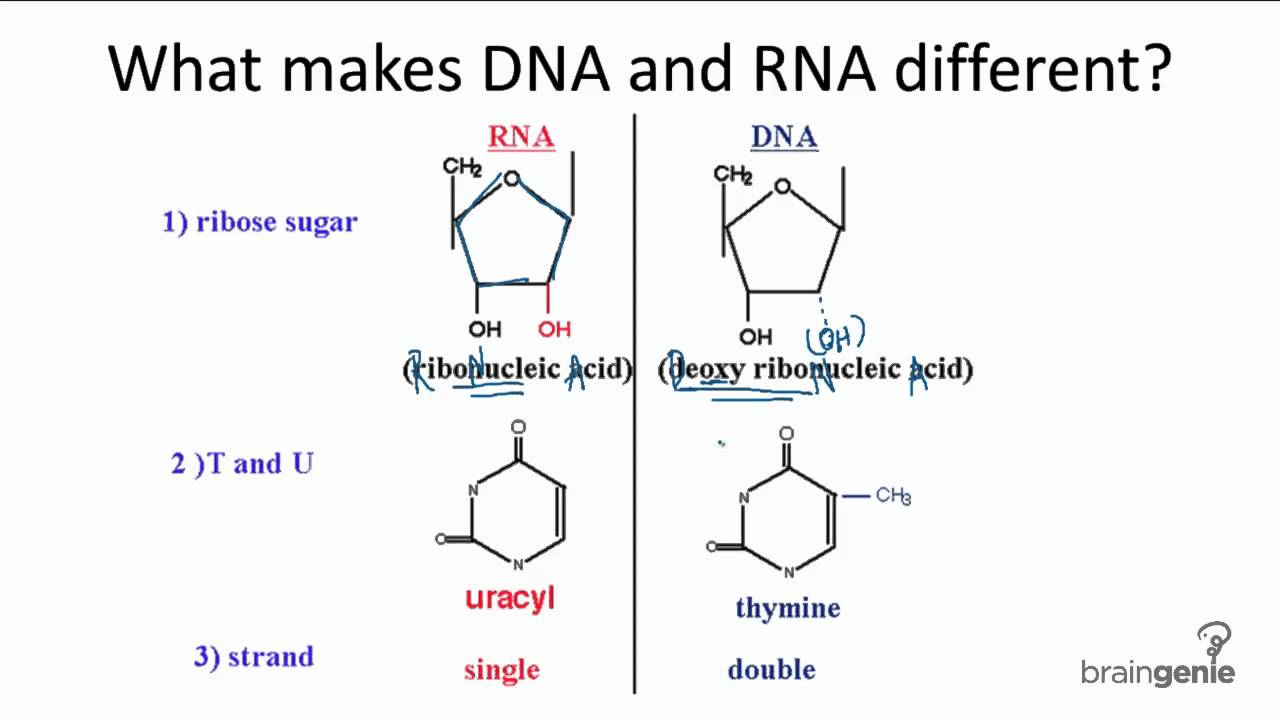



How Are Rna And Dna Different Socratic



Compbio Introduction And Basic Molecular Biology
Apr 21, 17 · Constructing a DNA Model Introduction DNA is a complex molecule that is found in all living organisms Constructing DNA models is a great way to learn about DNA structure, function and replication DNA contains the genetic information for the reproduction of life Its structure is that of a twisted double helix that is Continue reading "DNA Model"Regulation The structure of the molecule also allows DNA to make copies of itself Methods In this lab you will build a model DNA molecule and also model some of its functions I DNA Structure Use the paper model nucleotides provided to build a model of a DNAApplication Crick and Watson's elucidation of the structure of DNA using model making Skill Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to represent phosphates, pentoses and bases Guidance • In diagrams of DNA structure, the helical shape does not need to be shown, but the two strands should be




Dna And Rna Structure Function Expii




Dna Structure Vs Rna Structure Dna Stock Vector Royalty Free
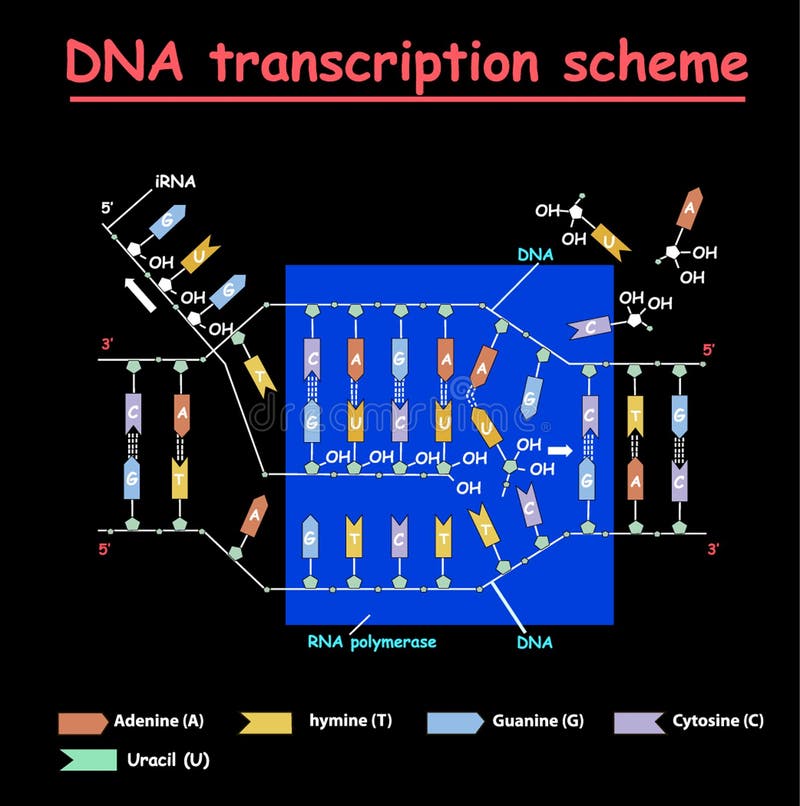
The chemical structure of RNA is very similar to that of DNA, but differs in three primary ways Unlike doublestranded DNA, RNA is a singlestranded molecule in many of its biological roles and consists of much shorter chains of nucleotides However, a single RNA molecule can, by complementary base pairing, form intrastrand double helixes, as in tRNA1 Building DNA and RNA Before mitosis begins, a cell doubles its amount of chromosomes by replicating, or copying all of its DNA During replication, doublestranded DNA unwinds and each strand acts as a template for a new strand DNA transcription is a similar process except only a part of the DNA sequence is copied to form a messenger RNARNA AND ITS STRUCTURE, FUNCTION AND TYPES With the discovery of the molecular structure of the DNA double helix in 1953, researchers turned to the structure of ribonucleic acid (RNA) as the next critical puzzle to be solved on the road



2 The Basic Structure Of Dna And Rna Dna Is Double Stranded Whereas Download Scientific Diagram




Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks
DNA and proteins are key molecules of the cell nucleus One gene makes one protein A gene is made of DNA Bacteria and viruses have DNA too The DNA molecule is shaped like a twisted ladder A half DNA ladder is a template for copying the whole RNA is an intermediary between DNA and protein DNA words are three letters longJun 02, 19 · The Structure of DNA In order to construct a model of DNA, you need to know what it looks like DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecule shaped like a twisted ladder or double helix The sides of the ladder are the DNA backbone, made up of repeating units of a pentose sugar (deoxyribose) bonded to a phosphate group11 rows · Dec 18, · Structure DNA consists of two strands, arranged in a double helix These strands are made up of




Nucleic Acid Definition Function Structure Types Britannica




Discovery Of Dna Double Helix Watson And Crick Learn Science At Scitable
There are several important differences between DNA and RNA 1) The sugar of RNA is always a ribose instead of a deoxyribose (with an extra hydroxyl group at carbon number 2 of the sugar) 2) the RNA molecule does not contain thymine bases;Jun 18, 08 · RNA has A,C,G and U Although both RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, there are key differences in the structure and function of RNA and DNA There are three types of RNA and each is involved in protein synthesis Protein synthesis is the process in which the correct amino acids are connected together in the order that is written on the gene 1An exploration of the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA If you want to learn more, join our free MITx #700x Introduction to Biology course (http//
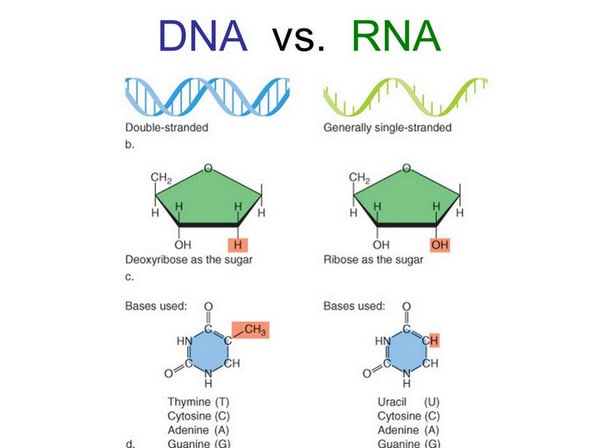



Difference Between Dna And Rna Laboratoryinfo Com




2 6 Structure Of Dna Rna Nucleic Acids




Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology
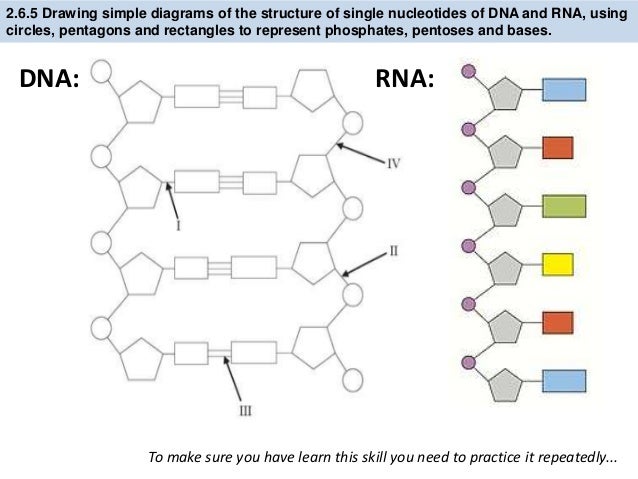



Ib Biology 2 6 7 1 Slides Dna Structure



Structure Of Dna And Rna




Structure Of Nucleic Acids Structure Of Dna Structure Of Rna Dna Structure And Rna Structure Youtube




Good Software For Dna Rna 3d Structure Prediction
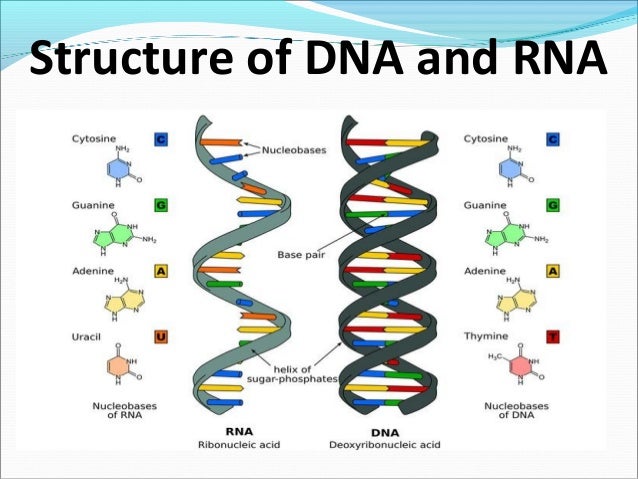



Structure Of Dna And Rna
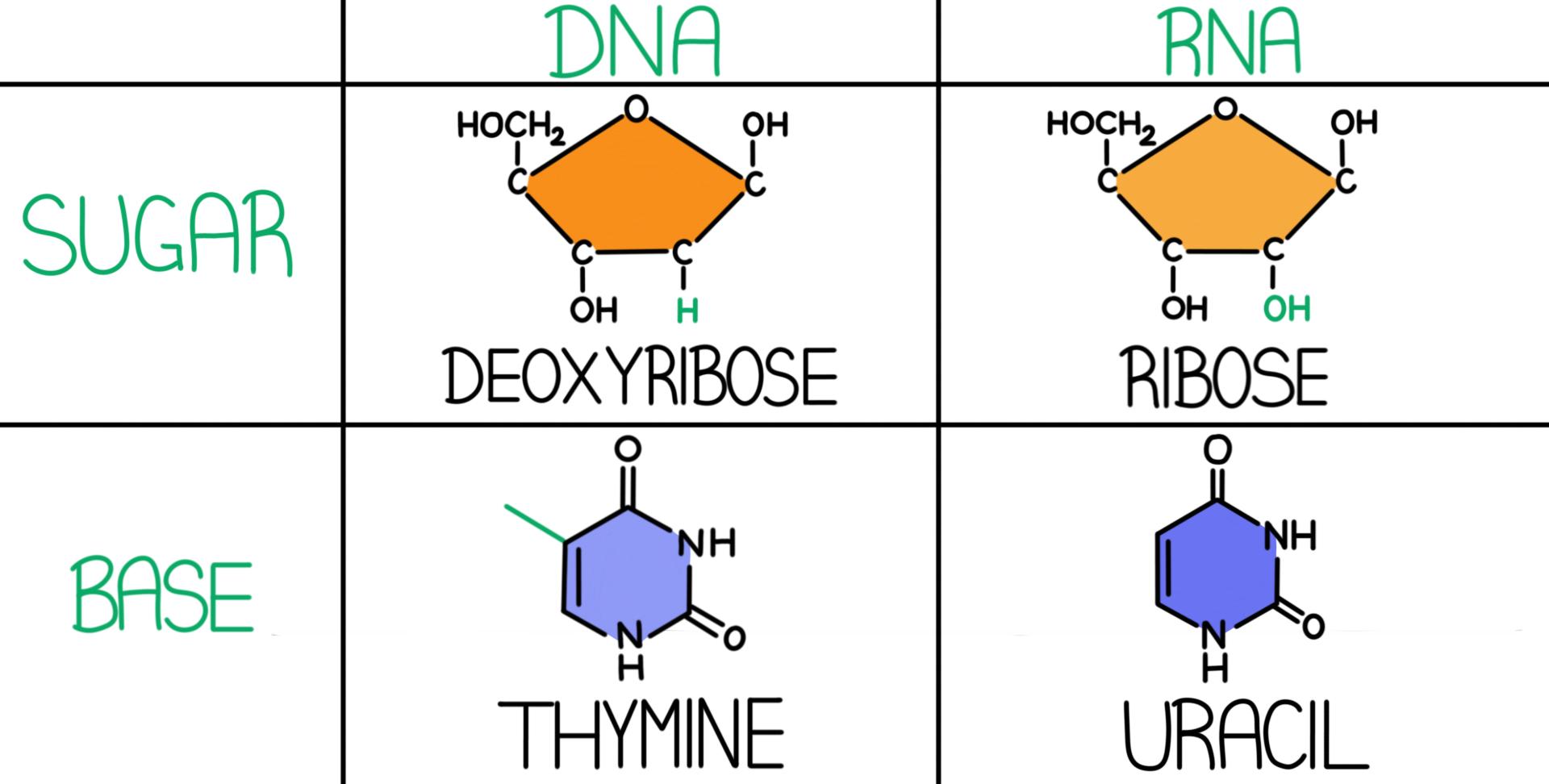



Dna Vs Rna Differences Similarities Expii




Discovery Of Dna Double Helix Watson And Crick Learn Science At Scitable
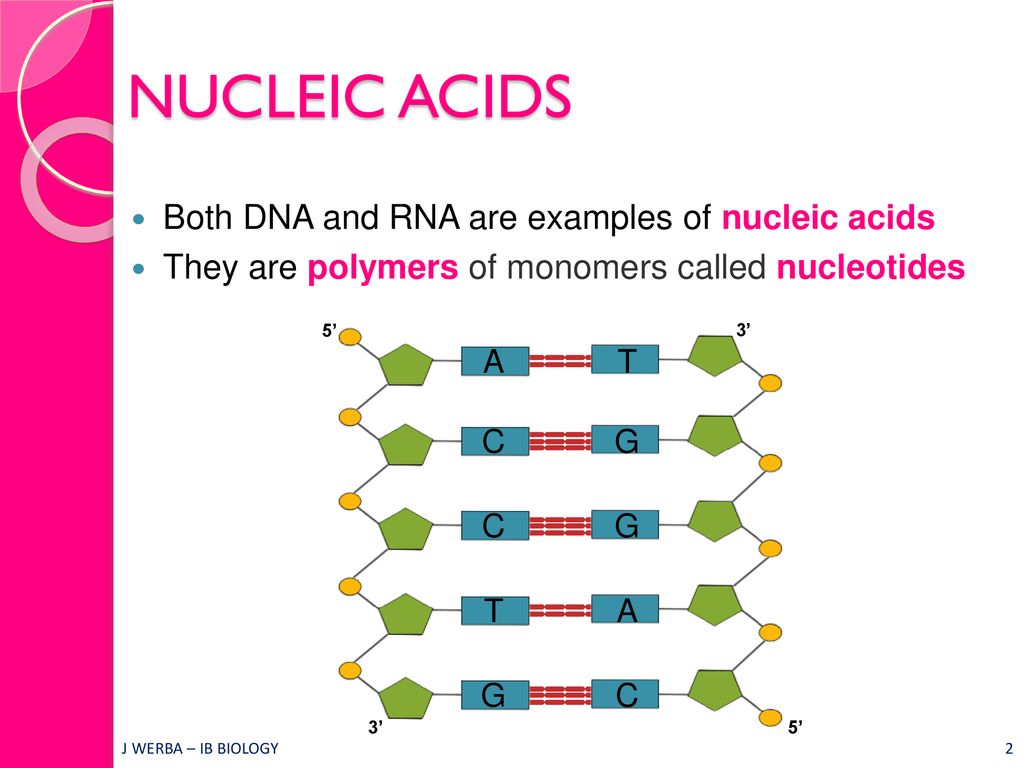



Revision Topics 2 6 2 7 Dna Rna Structure Dna Replication Ppt Download




Rna Double Helix Structure Identified Using Synchrotron Newsroom Mcgill University
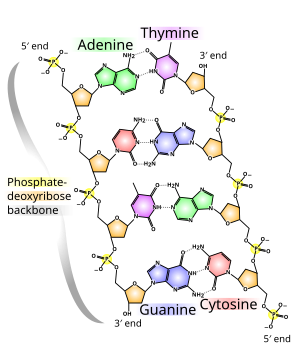



Dna Wikipedia



Structure Of Dna And Rna
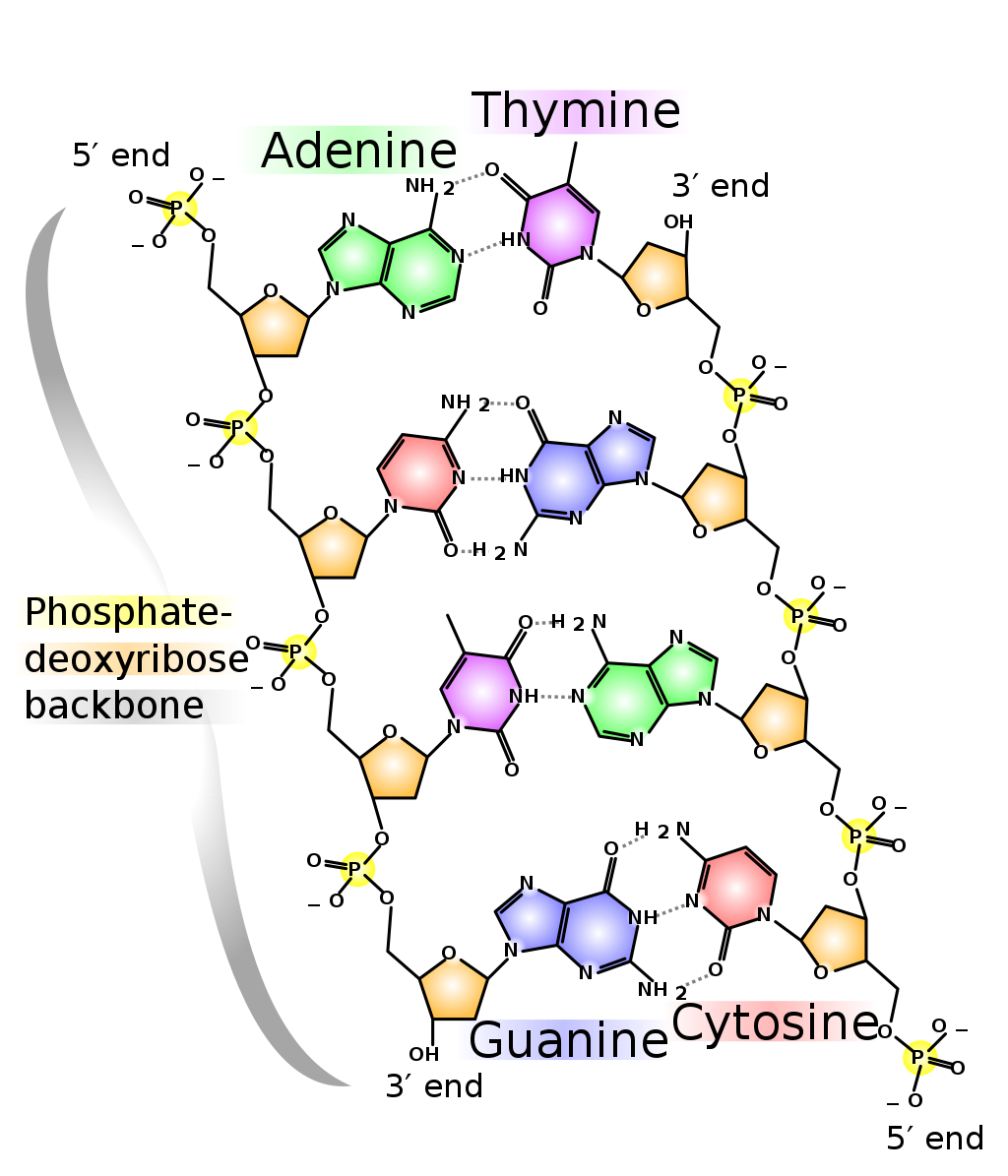



Dna And Rna Basics Replication Transcription And Translation



Q Tbn And9gcrcdbrmp X7uueldrntgn1aghsfylhvtvjstxzbay0 Usqp Cau



3




Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks




Dna Structure Model Anatomy Different Double Stock Vector Royalty Free



Rna Dna Secondary Structure Fold Viewer
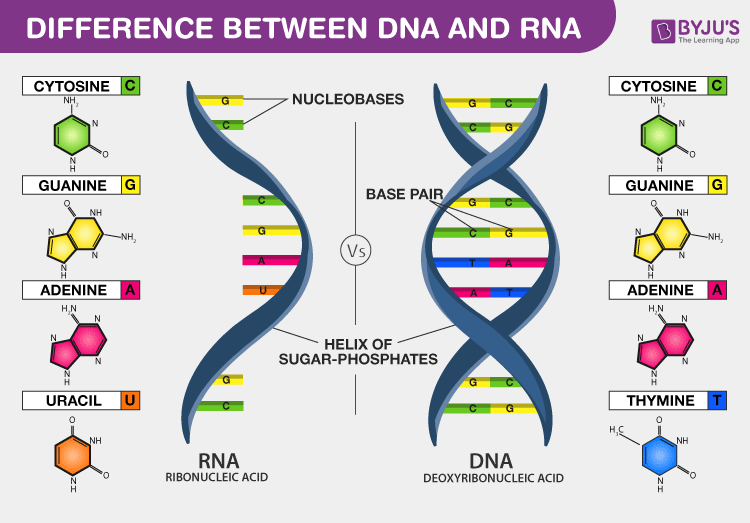



Dna Vs Rna Introduction And Differences Between Dna And Rna




Mit Edgerton Center Dna Rna Edgerton Center




Schematic Model Of The Double Helix Source Watson J The Structures Download Scientific Diagram




Scientific Biological Model Dna And Rna Transcription And Translation Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image



Dna And Rna Structures
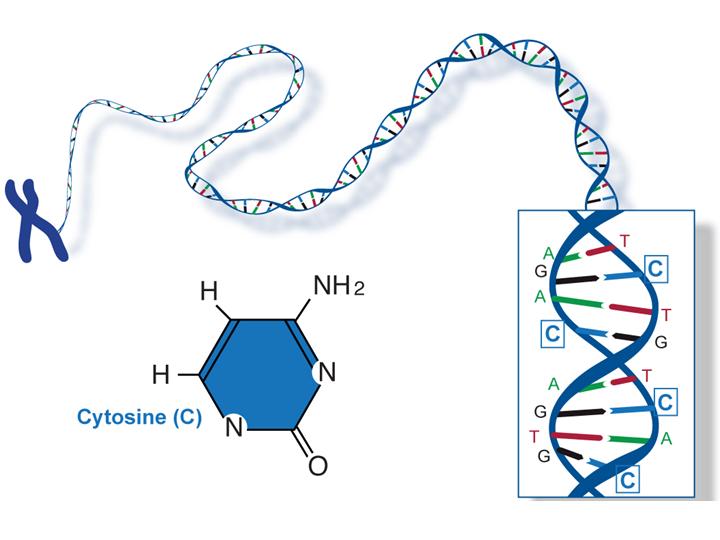



Fact Sheet Dna Rna Protein Microbenet The Microbiology Of The Built Environment Network




Nucleic Acids Structure Of Dna And Rna Dna Dna Structure Nucleic Acids Rna Rna Structure Glogster Edu Interactive Multimedia Posters
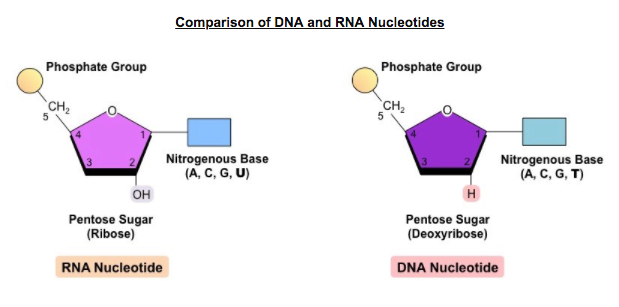



2 6 Dna Rna Structure




Nucleic Acids Dna And Rna Structure Youtube



Nucleotide



Dna Rna Structure Model India Manufacturers Suppliers Exporters In India



Rna Secondary Structure



Types Of Rna And How To Extract Or Purchase It Biochain Institute Inc




Dna Vs Rna Biology Dictionary




Dna Structure Vs Rna Structure Dna Stock Vector Royalty Free



The Differences Between Dna And Rna Explained With Diagrams Owlcation



Nucleic Acids Article Khan Academy




Dna And Rna Structure Practice Genetics Quiz Quizizz




Dna Model Paper Project Supports Distance Learning By Biology Roots




The Chemical Structure Of Dna Compound Interest




Dna Rna High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
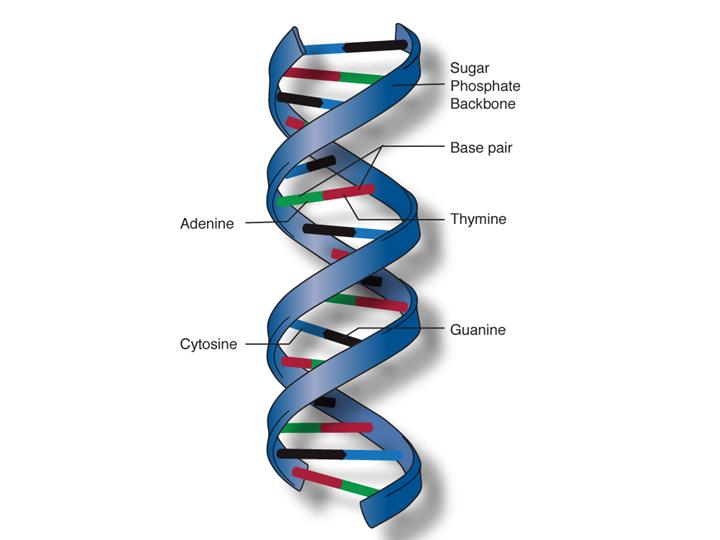



Fact Sheet Dna Rna Protein Microbenet The Microbiology Of The Built Environment Network




Dna And Rna Structure Function Expii
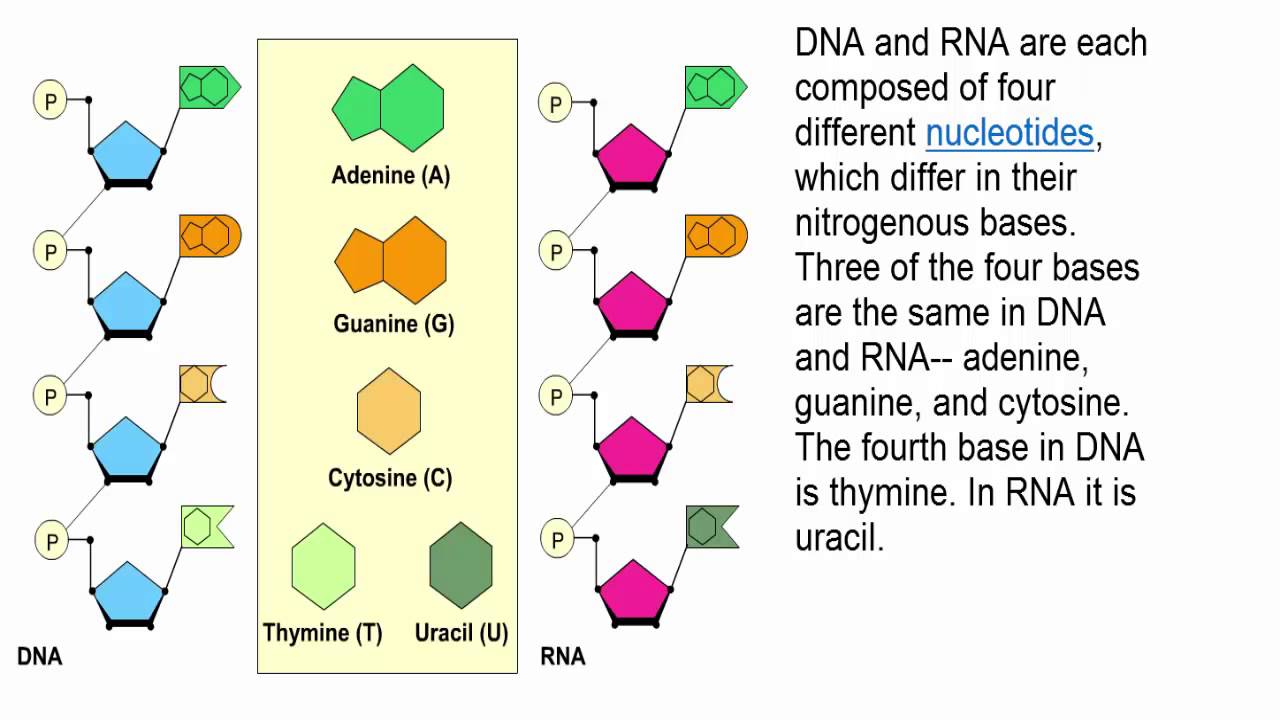



Dna And Rna Structure Youtube
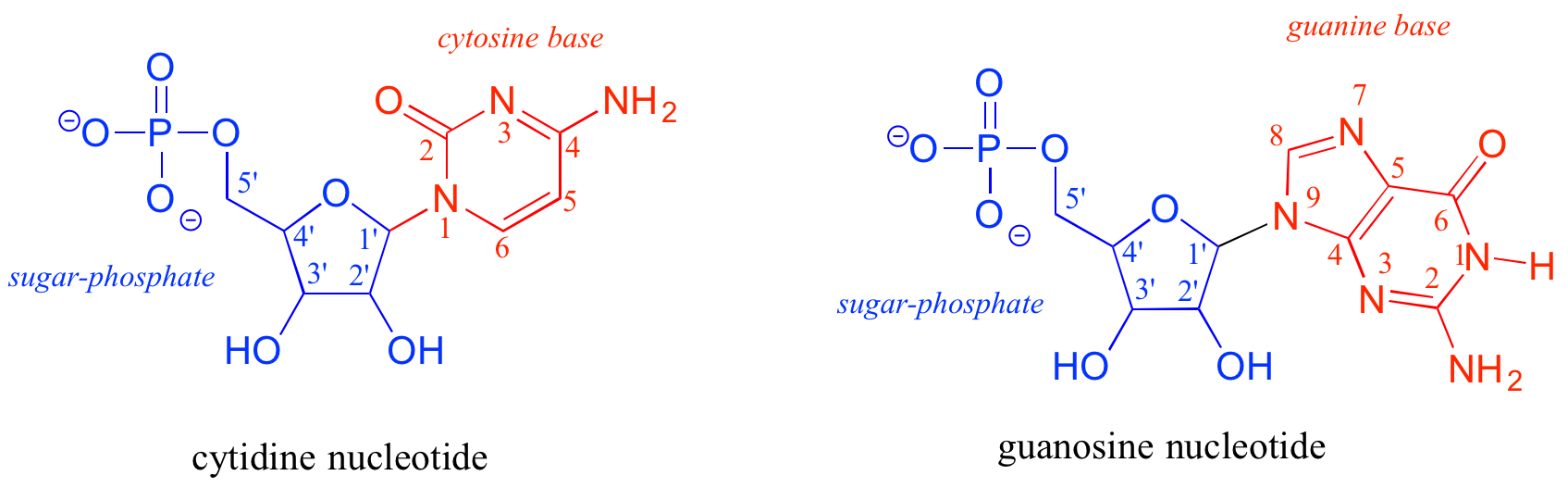



1 4 4 Introduction To Nucleic Acid Dna And Rna Structure Chemistry Libretexts
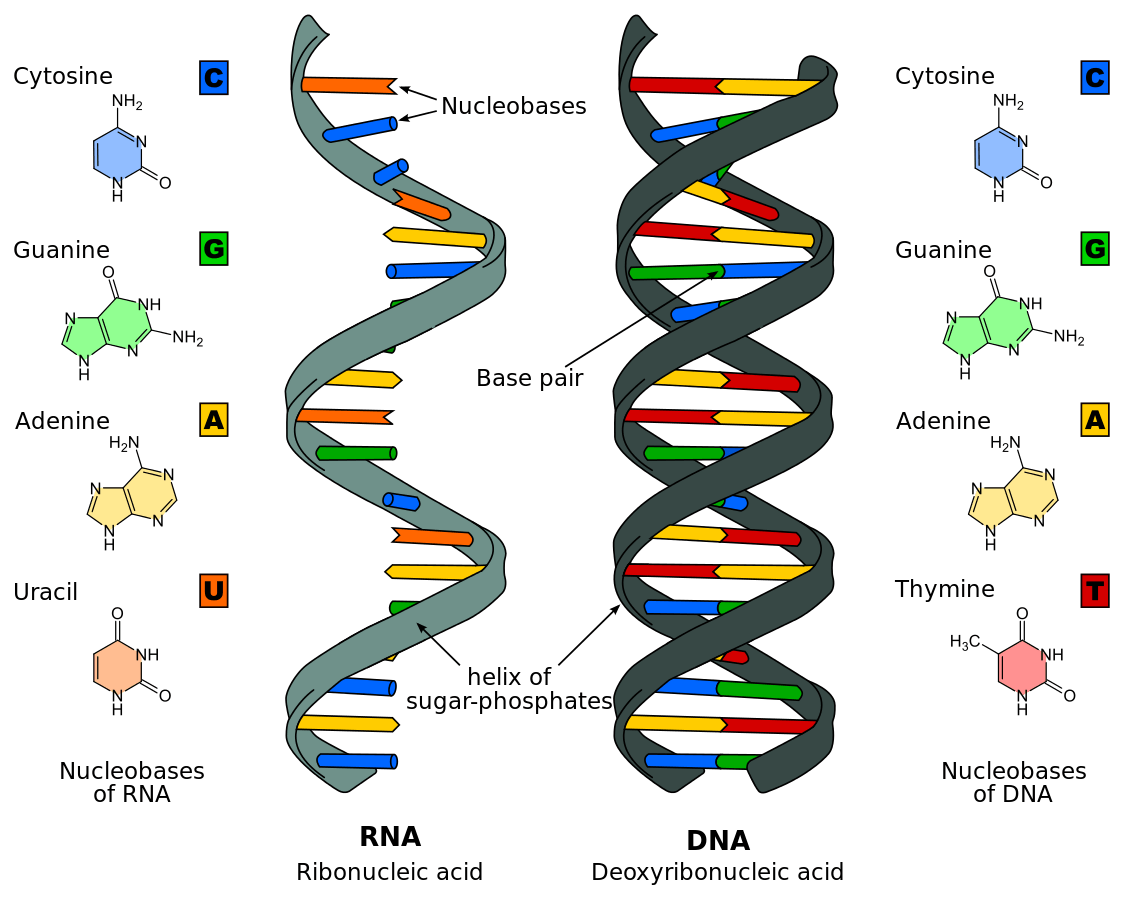



Dna And Rna Structure Function Expii



Rna Structure Stock Illustrations 4 322 Rna Structure Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




6 500 Dna Rna Stock Photos Pictures Royalty Free Images Istock




Structure Of Dna And Rna




Dna And Rna Structure And Function Youtube




Structural Differences Between Rna And Dna Coloring Page Free Printable Coloring Pages Color Worksheets Dna Dna Worksheet
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotides-5c253d8cc9e77c0001d9b089.jpg)



The Differences Between Dna And Rna



1 4 4 Introduction To Nucleic Acid Dna And Rna Structure Chemistry Libretexts




2 6 Structure Of Dna And Rna




6 500 Dna Rna Stock Photos Pictures Royalty Free Images Istock




Dna And Rna Structure Art Print Barewalls Posters Prints Bwc



Dochub Com Eveliasadullo Bzez1g M2 Unit 3 G10




Chemical Structure Of Dna Rna And Lna Download Scientific Diagram




2 6 Structure Of Dna And Rna Sl Hl 1 Biology 5 Ferguson



Solved 1 Several Enzymes And Proteins Participate In Dna Chegg Com




Dna Rna Structure Vector Photo Free Trial Bigstock



Dna And Rna Structure Royalty Free Vector Image
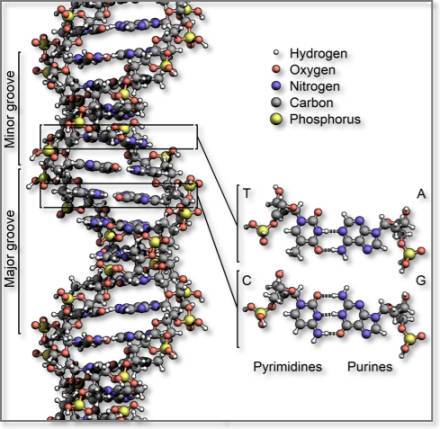



Dna And Rna Computational Medicine Center At Thomas Jefferson University



1




Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks




Dna Rna 3d Model



Structure Of Dna And Rna
/dna-versus-rna-608191_sketch_Final-54acdd8f8af04c73817e8811c32905fa.png)



The Differences Between Dna And Rna



Dna And Rna Structures
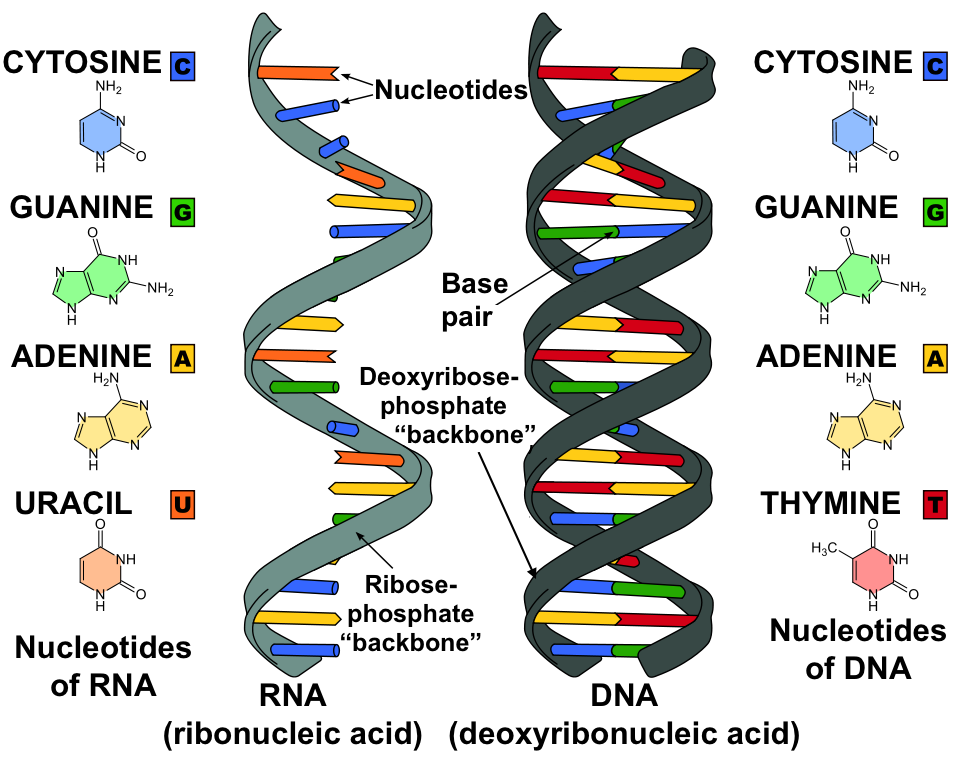



Rna And Protein Synthesis Review Article Khan Academy




Origins Of Cell Compartmentalization Ap Biology Biology Dictionary
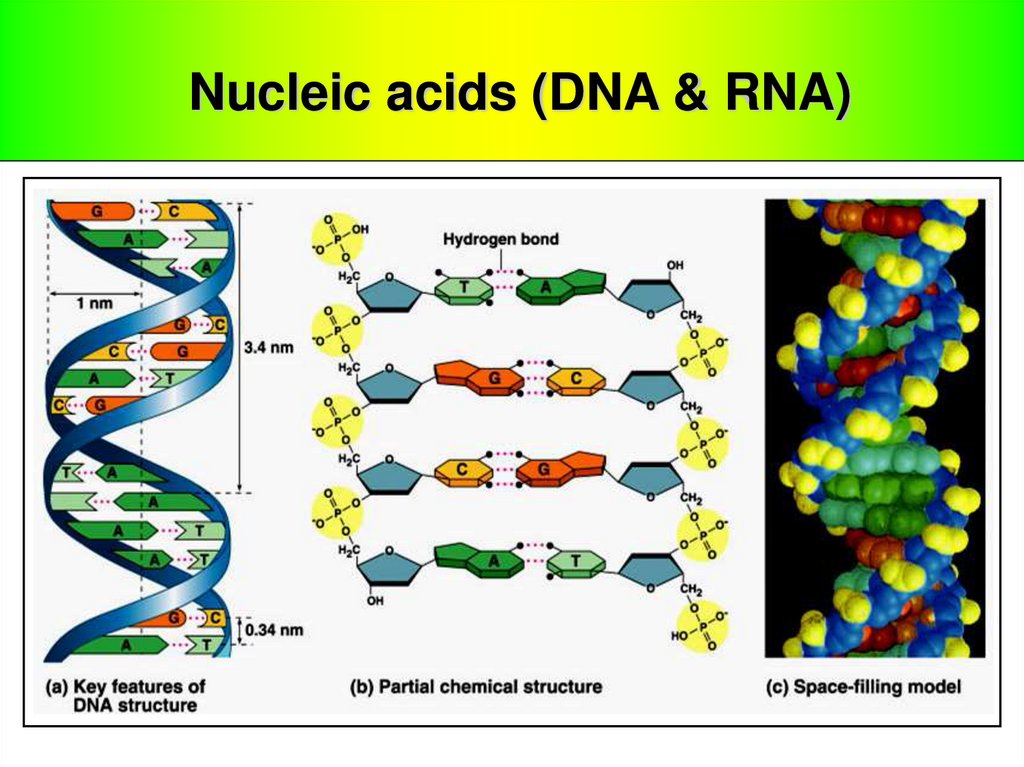



Nucleic Acids Dna Rna Online Presentation




Unit 4 Concept 1 Dna And Rna Structure Diagram Quizlet




Dna Vs Rna Difference And Comparison Diffen
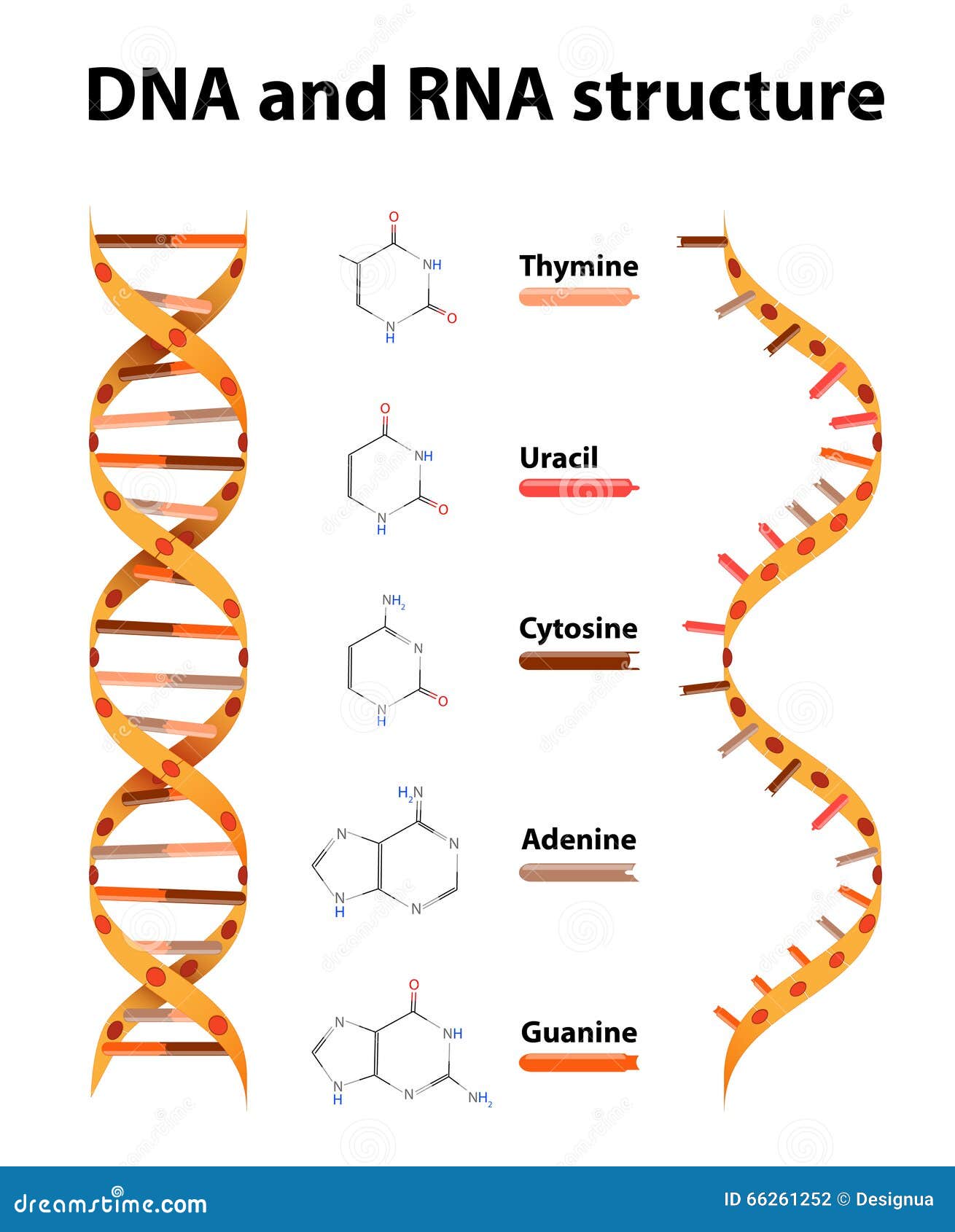



Rna Structure Stock Illustrations 4 322 Rna Structure Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/DNA-RNA-58dacf2e5f9b584683a1c375.jpg?w=640)



Structure Of Dna And Rna The Science Herald




Dna Vs Rna Biology Dictionary




Amazon Com 3b Scientific W Dna Rna Model 50cm Height Industrial Scientific
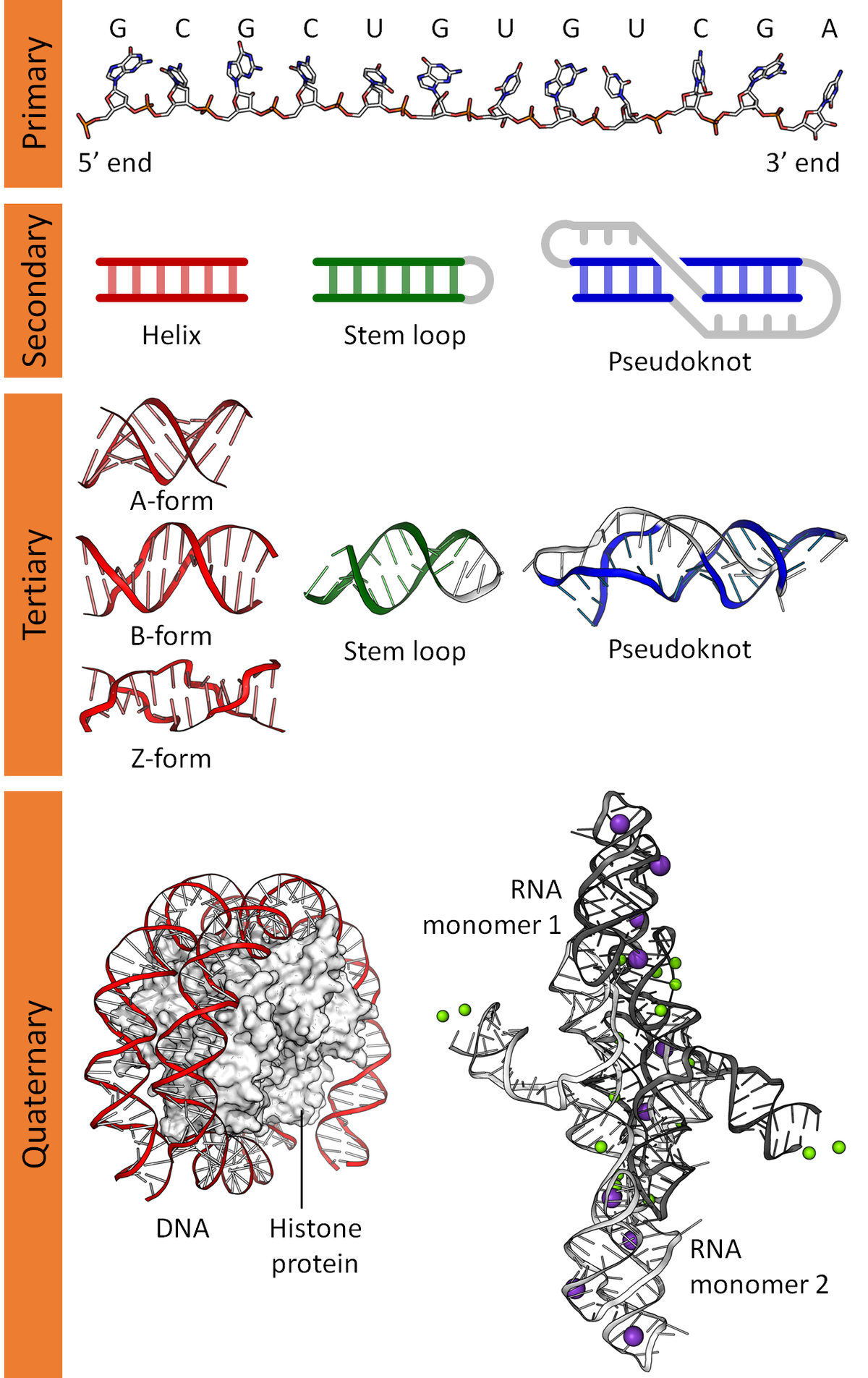



Nucleic Acid Structure Wikipedia
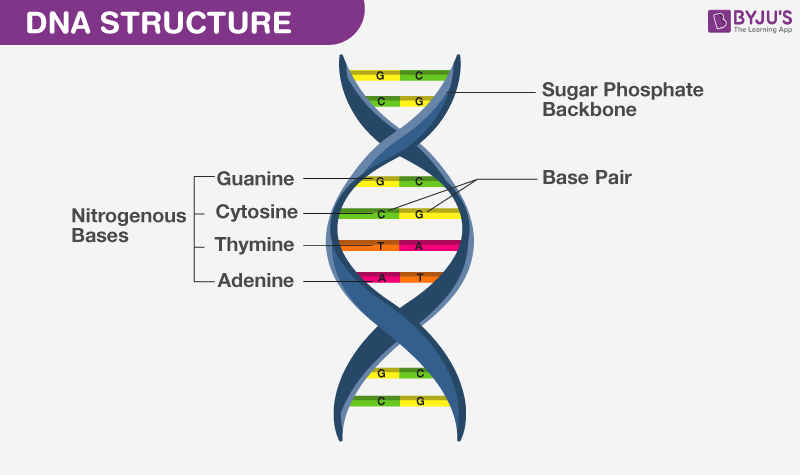



What Is Dna Meaning Dna Types Structure And Functions




2 6 Structure Of Dna And Rna Sl Hl 1 Biology 5 Ferguson
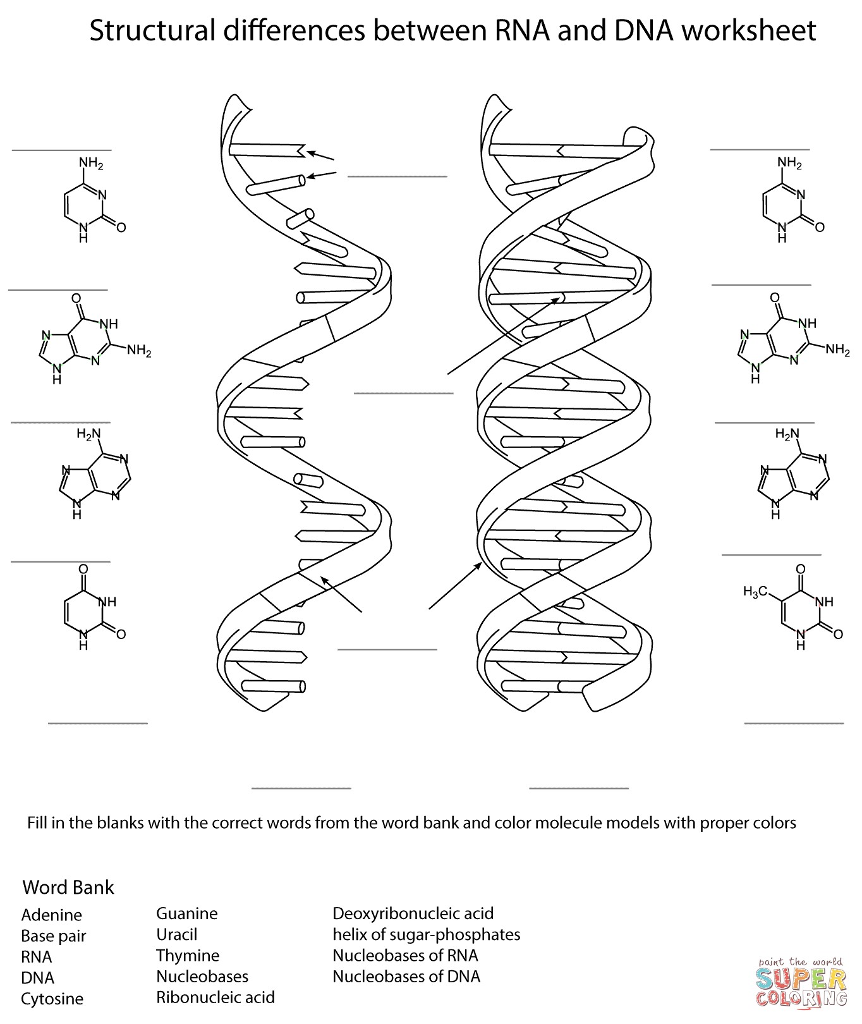



Solved Structural Differences Between Rna And Dna Workshe Chegg Com




Nucleic Acid Definition Function Structure Types Britannica




Nucleic Acid Secondary Structure Wikipedia
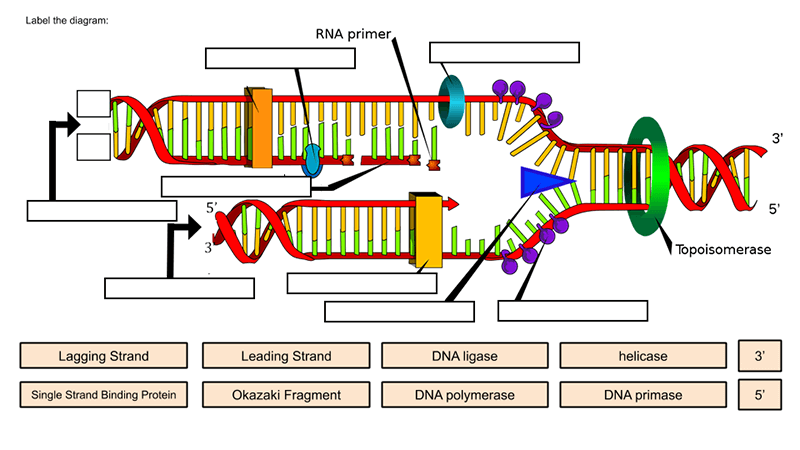



Dna Drag And Drop




What Are The Similarities Between Dna And Rna Albert Io



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿